In the ongoing fight against climate change, it is crucial to take proactive measures and implement effective strategies. The South East Councils Climate Change Alliance (SECCCA), a network of nine local governments to the South East of Melbourne, Australia, are at the forefront of this movement by taking the step to declare a climate emergency, recognising the urgent need to mitigate and reduce the impacts of climate change. SECCCA have embarked on a mission to identify and capitalise on carbon sequestration — the process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide — opportunities within the region. This case study explores their journey toward understanding, quantifying, and leveraging these opportunities, highlighting the crucial role played by Environmental Accounting Services (EAS).
The challenge: urgent action in the face of a climate emergency
SECCCA’s response to the climate emergency called for swift action to mitigate climate change impacts. Their first call of order was to explore the potential of carbon sequestration opportunities, which not only remove carbon from the atmosphere but also provide additional benefits such as biodiversity enhancement.
Knowing how to make the most of these, however, remained unclear. There was a significant knowledge gap regarding existing and potential future carbon sequestration opportunities within the region. Similarly, the intricacies of carbon credit and offset opportunities that the carbon sequestration project would provide were not well understood. This is where EAS’ experience and expertise came in.
The approach: a systematic journey
EAS adopted a comprehensive approach to address SECCCA’s challenges. It included:
Stakeholder engagement: EAS began by engaging key stakeholders and seeking local insights and experiences. This initial step allowed for collecting valuable input that would inform the subsequent analysis of available carbon sequestration opportunities.
Literature review: An extensive literature review was conducted by EAS, delving into the realms of carbon sequestration and market conditions. This encompassed an exploration of trends, projected costs, reliability, risks, and the availability of these opportunities.
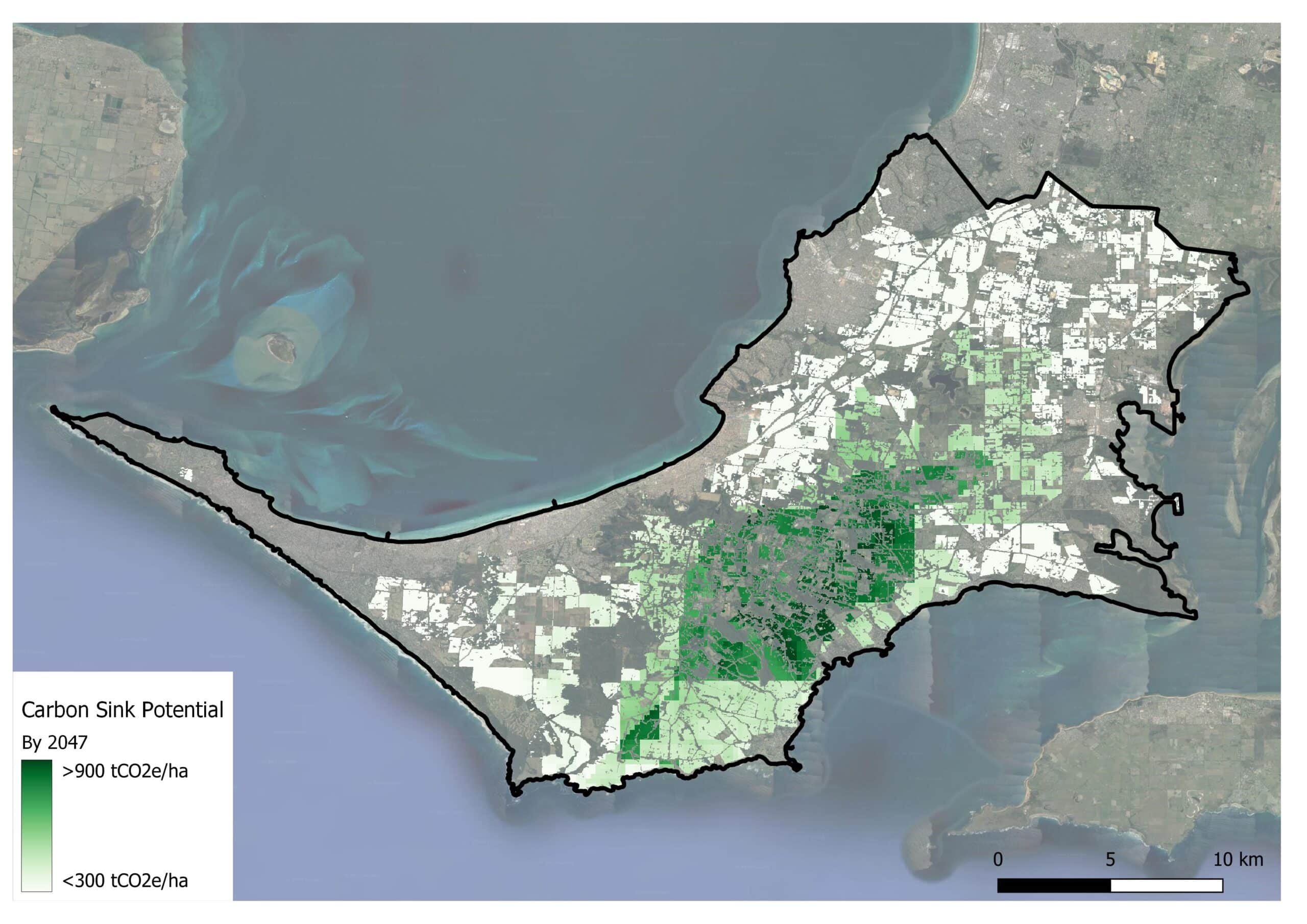
Quantification: EAS meticulously quantified the carbon sequestration potential of identified areas within the SECCCA region using various methodologies under the Australian Carbon Credit Unit (ACCU) Scheme (formerly known as the Emissions Reduction Fund), spanning native plantings, plantation forestry, soil carbon, and blue carbon. Using the FLINTpro model, the carbon sequestration potential of the focussed methodology, environmental (native) plantings, was spatially modelled over a 25-year period.
Cost-benefit analysis: EAS provided a thorough analysis, including cost-benefit assessments, case study examples, and a decision-making framework. The results of this analysis and framework developed, provides the councils with material and information to evaluate carbon sequestration opportunities effectively, providing a clear path forward.
The results: informed carbon sequestration opportunities
The collaboration between SECCCA and EAS produced substantial and impactful results, including:
Informed stakeholders: The project deliverables showcased exceptional quality, enriched by the valuable insights and local expertise of stakeholders. This deepened the understanding of carbon sequestration opportunities and ensured that all relevant perspectives were considered.
Quantified potential: EAS quantified the carbon sequestration potential within the SECCCA region, providing councils with the knowledge to enable well-informed decision-making to guide investments in carbon sequestration projects. providing councils with a tangible foundation upon which to base their decisions. This quantification allowed for informed and data-driven choices in pursuing carbon sequestration initiatives.
Empowered decision-making: The information and tools supplied by EAS equipped SECCCA with the resources needed to make informed decisions regarding carbon sequestration opportunities. These resources paved the way for the sustainable acquisition of environmental and social benefits.
Project readiness: EAS streamlined the path to project implementation by presenting a summary of project requirements, cost-benefit analysis, and illustrative case study examples. This readiness framework ensured that councils were well-prepared to embark on successful carbon sequestration projects.
Unleashing success through collaboration
During our partnership with SECCCA to achieve its emission and climate mitigation objectives, our commitment to the cause was affirmed by Principal Climate Adaptations Officer with the City of Port Phillip, Renae Walton. She acknowledged our efforts by stating, “The team executed the project well. They were great with following up on feedback and presenting the information in a clear and succinct way.”
SECCCA’s commitment to addressing climate change through carbon sequestration initiatives, coupled with the expertise and guidance provided by EAS, stands as a testament to the power of informed action in the fight against climate change. The approach taken and the results achieved exemplify the effectiveness of a systematic and collaborative approach to environmental challenges, and we are excited to see the ongoing positive impacts of this initiative.